Sleep Science Explained: Understanding Your Body's Rest & Recovery System

Why Understanding Sleep Science Matters
Sleep isn’t just “time off” for your brain and body. It’s an active, highly organized biological process during which your body:
- Consolidates memories from short-term to long-term storage
- Repairs tissues and builds new cells
- Detoxifies the brain through the glymphatic system
- Regulates hormones that control hunger, stress, and growth
- Strengthens immune function to fight off illness
Understanding these processes helps you optimize your sleep environment and habits for maximum restoration and performance.
🧠 The Four Stages of Sleep: Your Nightly Journey
Every night, your brain cycles through distinct stages, each serving crucial biological functions.
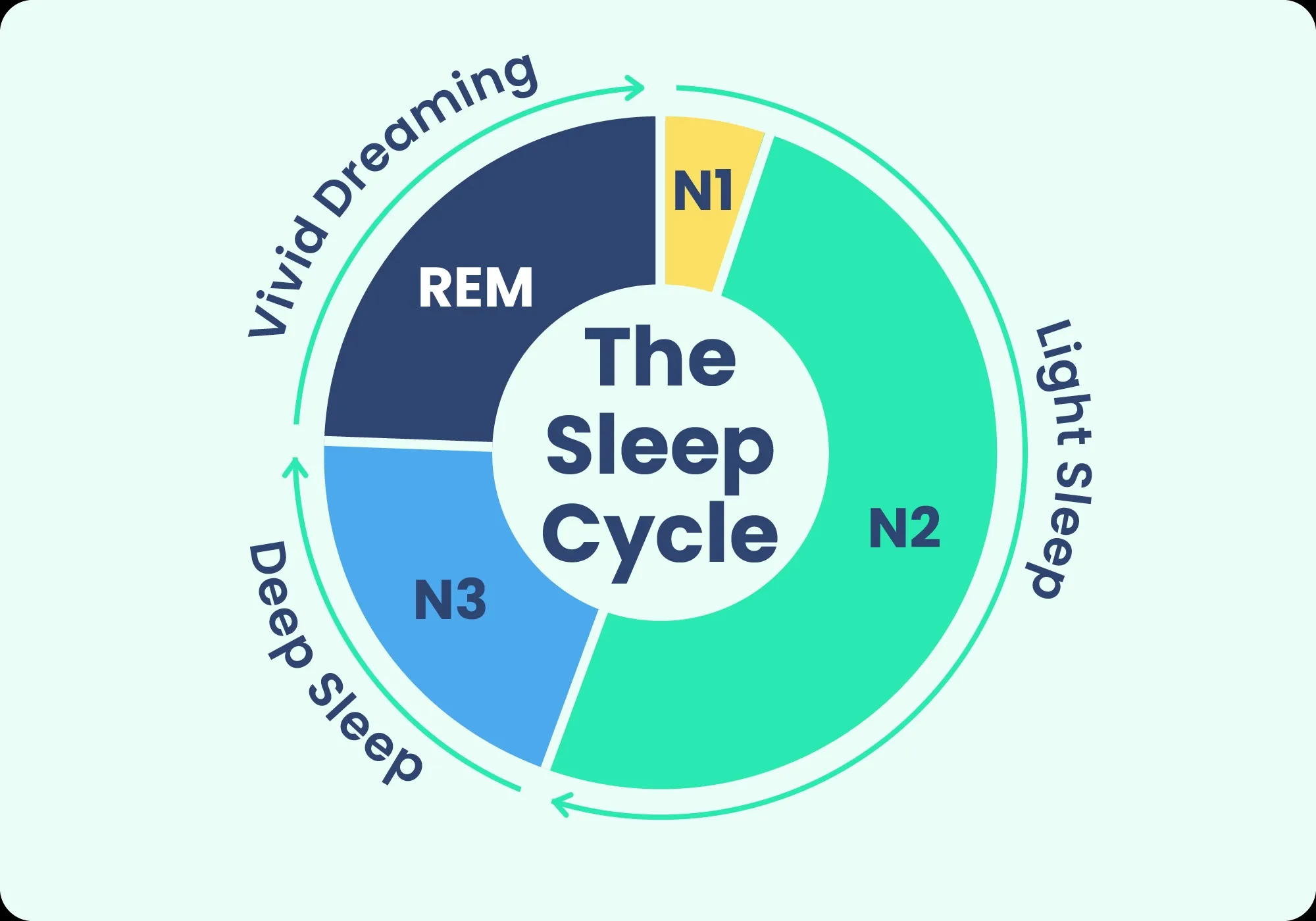
Stage 1: Light Sleep (5% of total sleep)
Duration: 5-10 minutes
Brain Waves: Alpha to Theta (4-8 Hz)
What Happens:
- Transition from wakefulness to sleep
- Muscle activity slows down
- Easy to wake up
- May experience hypnic jerks
Optimization Tip: Keep your bedroom cool (65-68°F) to help your body temperature drop naturally.
Stage 2: True Sleep (45% of total sleep)
Duration: 10-25 minutes (first cycle)
Brain Waves: Sleep spindles and K-complexes
What Happens:
- Heart rate and breathing slow
- Body temperature drops
- Brain activity decreases
- Memory consolidation begins
Optimization Tip: Use blackout curtains or an eye mask to prevent light from disrupting this crucial stage.
Stage 3: Deep Sleep (25% of total sleep)
Duration: 20-40 minutes (first cycle)
Brain Waves: Delta waves (0.5-4 Hz)
What Happens:
- Physical restoration: Growth hormone release
- Tissue repair: Muscle and bone growth
- Immune strengthening: White blood cell production
- Brain detox: Amyloid plaque removal
Why It’s Critical: Deep sleep is when your body does its most important repair work. Lack of deep sleep leads to:
- Weakened immune system
- Poor physical recovery
- Increased inflammation
- Memory problems
Optimization Tip: Avoid alcohol and caffeine 6 hours before bed - both suppress deep sleep stages.
Stage 4: REM Sleep (25% of total sleep)
Duration: Increases throughout the night
Brain Waves: Similar to wakefulness
What Happens:
- Vivid dreaming and emotional processing
- Memory consolidation for learning and creativity
- Brain development and neural pathway strengthening
- Neurotransmitter regulation for mood stability
Optimization Tip: Get 7-9 hours total sleep to ensure adequate REM - it occurs more in the final hours.
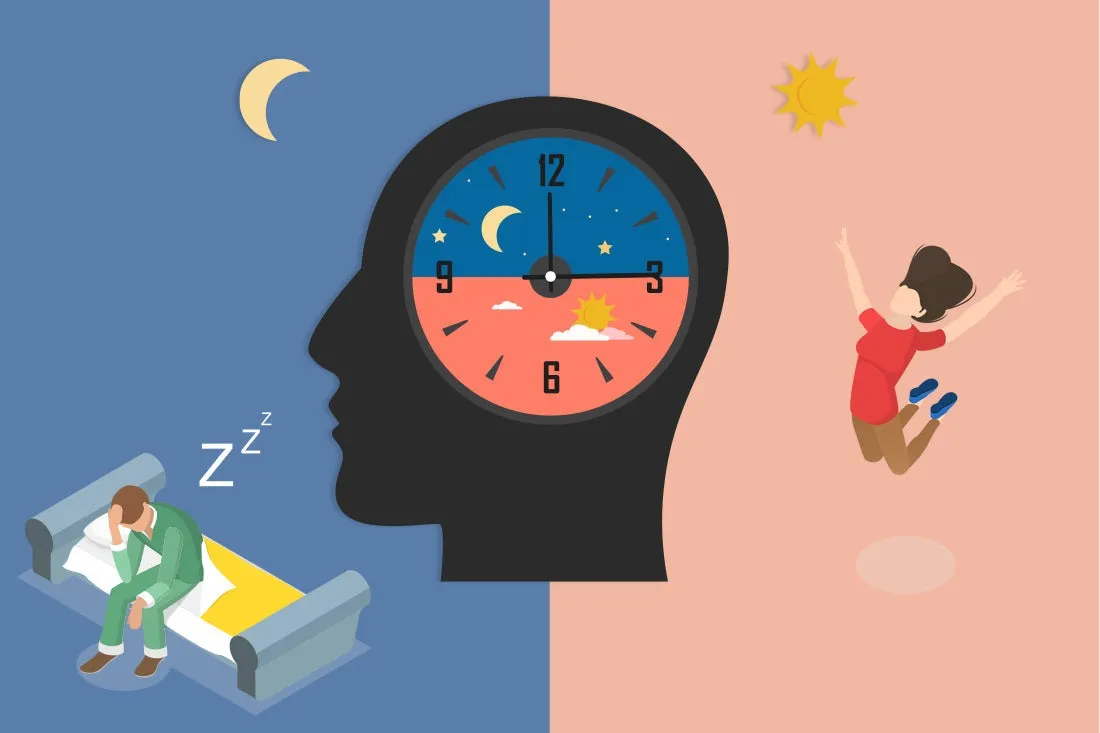
⏰ Your Circadian Rhythm: The Internal Clock
Your circadian rhythm is a 24-hour biological clock controlled by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in your brain. It regulates:
Key Circadian Hormones
Melatonin (The Sleep Hormone):
- Rises around 9 PM
- Peaks between 2-4 AM
- Suppressed by light exposure
- Signals sleepiness to the body
Cortisol (The Alertness Hormone):
- Peaks around 8 AM
- Gradually decreases throughout day
- Lowest levels during deep sleep
- Chronic elevation disrupts sleep
Growth Hormone:
- Released primarily during deep sleep
- Peak production: 10 PM - 2 AM
- Essential for tissue repair and metabolism
Light’s Powerful Effect on Sleep
Blue Light (400-490 nm wavelength):
- Most potent circadian disruptor
- Suppresses melatonin production
- Found in: Phones, computers, LED lights, TV screens
Research Finding: Just 1 hour of blue light exposure before bed can delay sleep onset by 3 hours and reduce REM sleep by 23%.
Natural Light Therapy:
- Morning sunlight (10,000+ lux) resets circadian rhythm
- Evening dim light (< 50 lux) promotes melatonin
- Consistent light exposure times strengthen circadian signals
🔬 The Glymphatic System: Your Brain’s Cleanup Crew
Discovered in 2012, the glymphatic system is your brain’s waste removal network that primarily activates during deep sleep.
How It Works
- Brain cells shrink by 60% during deep sleep
- Cerebrospinal fluid flows through expanded gaps
- Toxic proteins get flushed including amyloid-beta and tau
- Waste exits through lymphatic vessels
What Gets Cleaned Out
- Amyloid-beta plaques (linked to Alzheimer’s disease)
- Tau proteins (associated with dementia)
- Metabolic waste from daily brain activity
- Inflammatory molecules that cause cognitive decline
Research Insight: People who consistently get less than 6 hours of sleep have 50% more amyloid-beta buildup in their brains.
Sleep Position Matters
Side sleeping (particularly left side) enhances glymphatic clearance by:
- Improving cerebrospinal fluid flow
- Reducing compression on lymphatic vessels
- Optimizing gravity-assisted drainage
🏃♂️ Sleep and Physical Performance
Sleep directly impacts every aspect of physical performance through multiple biological mechanisms.
Muscle Recovery and Growth
Growth Hormone Release:
- 70% occurs during deep sleep stages
- Peak production: First 3 hours of sleep
- Essential for muscle protein synthesis
- Stimulates tissue repair and regeneration
Testosterone Production:
- Primarily produced during REM sleep
- Levels drop 15% after one night of poor sleep
- Critical for muscle building and recovery
- Affects motivation and energy levels
Athletic Performance Studies
Stanford Basketball Study:
- Players extended sleep to 10 hours/night for 5-7 weeks
- Free throw accuracy improved 11.4%
- Three-point accuracy improved 13.7%
- Sprint times improved significantly
Tennis Serve Study:
- Sleep-deprived players (4 hours) vs. rested (8 hours)
- Serve accuracy decreased 53%
- Reaction time slowed 18%
- Perceived effort increased 22%
🧪 Sleep and Cognitive Function
Sleep is essential for multiple cognitive processes, particularly memory consolidation and creative thinking.
Memory Formation Process
Stage 2 Sleep:
- Declarative memories (facts, events) transfer from hippocampus to cortex
- Sleep spindles correlate with memory retention strength
- Memory replay occurs at 6-7x normal speed
REM Sleep:
- Procedural memories (skills, habits) get strengthened
- Creative connections form between disparate concepts
- Emotional memories get processed and integrated
The Forgetting Function
Sleep doesn’t just strengthen important memories - it actively weakens unnecessary ones through:
- Synaptic downscaling - reducing connection strength
- Selective forgetting - clearing irrelevant information
- Memory integration - combining related experiences
This process prevents cognitive overload and improves learning capacity.
Creativity and Problem-Solving
REM Sleep Benefits:
- Increases remote associations by 33%
- Enhances insight problem-solving
- Facilitates “aha!” moments upon waking
- Improves flexible thinking
Famous Examples:
- Kekulé discovered benzene ring structure in a dream
- Tesla visualized AC motor during sleep
- Mendeleev completed periodic table after dream
🏥 Health Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation (< 6 hours nightly) creates cascading health problems across multiple body systems.
Immune System Suppression
Research Findings:
- People sleeping < 6 hours are 3x more likely to catch a cold
- Flu vaccine effectiveness drops 50% with inadequate sleep
- Natural killer cell activity decreases 70% after one sleepless night
- Chronic inflammation markers increase significantly
Metabolic Disruption
Hormonal Changes:
- Ghrelin (hunger hormone) increases 28%
- Leptin (satiety hormone) decreases 18%
- Insulin sensitivity drops 30%
- Cortisol levels remain elevated
Weight Gain Risk:
- Short sleepers gain 55% more weight over 15 years
- Risk of obesity increases 89% in children, 30% in adults
- Cravings for high-calorie foods increase dramatically
Cardiovascular Impact
Blood Pressure:
- Rises 5-15 mmHg with chronic sleep loss
- “Non-dipping” pattern during sleep increases heart disease risk
- Recovery requires 2-3 nights of adequate sleep
Heart Disease Risk:
- Increases 48% with < 6 hours nightly
- Stroke risk increases 15% per hour of sleep lost
- Irregular heartbeat patterns emerge
💡 Evidence-Based Sleep Optimization Strategies
Based on sleep science research, here are the most effective ways to improve your sleep quality:
Temperature Regulation
Core Body Temperature:
- Drops 2-3°F naturally before sleep
- Cooling signals sleepiness to the brain
- Room temperature: 65-68°F (18-20°C) optimal
- Warm bath 90 minutes before bed helps cooling
Light Management
Morning Light:
- Get 10,000+ lux within 1 hour of waking
- Use bright light therapy box if needed
- Exposure resets circadian rhythm daily
Evening Light:
- Dim lights to < 50 lux after sunset
- Use blue light blocking glasses if needed
- Consider amber bulbs in bedroom
Timing Strategies
Sleep Schedule:
- Consistent bedtime/wake time (±30 minutes)
- Earlier schedule generally better than late
- Weekend sleep-ins shouldn’t exceed 1 hour
Exercise Timing:
- Vigorous exercise 3+ hours before bed
- Light stretching/yoga 1 hour before bed okay
- Morning exercise strengthens circadian rhythm
🔬 Cutting-Edge Sleep Research
Sleep Tracking Technology
Polysomnography (Gold Standard):
- Measures brain waves, eye movements, muscle activity
- Used in sleep labs for diagnosis
- Most accurate but not practical for home use
Consumer Wearables:
- Track movement, heart rate variability
- 60-70% accurate for sleep/wake detection
- Helpful for trends but not precise staging
Promising Technologies:
- Radar-based systems for contactless monitoring
- Smart mattresses with embedded sensors
- EEG headbands for detailed brainwave analysis
Emerging Sleep Therapies
Targeted Memory Reactivation:
- Playing specific sounds during slow-wave sleep
- Enhances memory consolidation for learned material
- Potential applications in education and therapy
Transcranial Stimulation:
- Electrical stimulation during deep sleep
- Increases slow-wave activity by 40%
- May improve memory and cognitive function
Chronotherapy:
- Light therapy timed to circadian phase
- Personalized based on genetic chronotype
- More effective than generic sleep hygiene
🎯 Key Takeaways for Better Sleep
- Prioritize Deep Sleep - It’s when your body does its most important restoration work
- Respect Your Circadian Rhythm - Consistent sleep/wake times are more important than total hours
- Optimize Your Environment - Cool, dark, quiet bedroom enhances all sleep stages
- Time Your Light Exposure - Bright mornings, dim evenings strengthen your internal clock
- Think Long-Term - Chronic sleep patterns matter more than occasional bad nights
Remember: Sleep is not a luxury - it’s a biological necessity for optimal health, performance, and longevity. Every hour of sleep you invest pays dividends in every area of your life.
📚 Recommended Resources
Books:
- “Why We Sleep” by Matthew Walker, PhD
- “The Sleep Solution” by Chris Winter, MD
- “The Circadian Code” by Satchin